How Ballistic Coefficent Varies with Twist Rate (Stabilization)
By Bryan Litz, Applied Ballistics
 Last month, in the Daily Bulletin, we talked about twist rate and muzzle velocity. That discussion was based on a detailed study published in Modern Advancements in Long Range Shooting.
Last month, in the Daily Bulletin, we talked about twist rate and muzzle velocity. That discussion was based on a detailed study published in Modern Advancements in Long Range Shooting.
More Spin, Less Drag
In this article, we look at how twist rate and stability affect the Ballistic Coefficient (BC) of a bullet. Again, this topic is covered in detail in the Modern Advancements book. Through our testing, we’ve learned that adequate spin-stabilization is important to achieving the best BC (and lowest drag). In other words, if you don’t spin your bullets fast enough (with sufficient twist rate), the BC of your bullets may be less than optimal. That means, in practical terms, that your bullets drop more quickly and deflect more in the wind (other factors being equal). Spin your bullets faster, and you can optimize your BC for best performance.
Any test that’s designed to study BC effects has to be carefully controlled in the sense that the variables are isolated. To this end, barrels were ordered from a single barrel smith, chambered and headspaced to the same rifle, with the only difference being the twist rate of the barrels. In this test, 3 pairs of barrels were used. In .224 caliber, 1:9” and 1:7” twist. In .243 caliber it was 1:10” and 1:8”, and in .30 caliber it was 1:12” and 1:10”. Other than the twist rates, each pair of barrels was identical in length, contour, and had similar round counts. Here is a barrel rack at the Applied Ballistics Lab:
Applied Ballistics used multiple barrels to study how twist rate affects BC.

“The Modern Advancements series is basically a journal of the ongoing R&D efforts of the Applied Ballistics Laboratory. The goal of the series is to share what we’re learning about ballistics so others can benefit.” –Bryan Litz
Barrel twist rate along with velocity, atmospherics, and bullet design all combine to result in a Gyroscopic Stability Factor (SG). It’s the SG that actually correlates to BC. The testing revealed that if you get SG above 1.5, the BC may improve slightly with faster twist (higher SG), but it’s very difficult to see. However, BC drops off very quickly for SGs below 1.5. This can be seen in the figure below from Modern Advancements in Long Range Shooting.
The chart shows that when the Gyroscopic Stability Factor (SG) is above 1.5, BC is mostly constant. But if SG falls below 1.5, BC drops off dramatically.
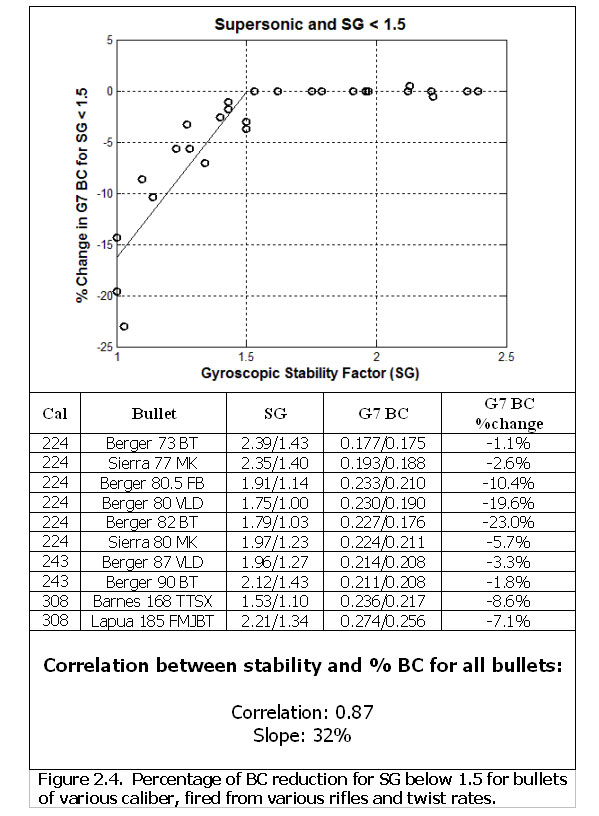
Note that the BC drops by about 3% for every 0.1 that SG falls below 1.5. The data supports a correlation coefficient of 0.87 for this relationship. That means the 3% per 0.1 unit of SG is an accurate trend, but isn’t necessarily exact for every scenario.
It’s a common assumption that if a shooter is seeing great groups and round holes, that he’s seeing the full potential BC of the bullets. These tests did not support that assumption. It’s quite common to shoot very tight groups and have round bullet holes while your BC is compromised by as much as 10% or more. This is probably the most practical and important take-away from this test.
To calculate the SG of your bullets in your rifle, visit the Berger Bullets online stability calculator. This FREE calculator will show you the SG of your bullets, as well as indicate if your BC will be compromised (and by how much) if the SG is below 1.5. With the stated twist rate of your barrel, if your selected bullet shows an SG of 1.5 (or less), the calculator will suggest alternate bullets that will fully stabilize in your rifle. This valuable online resource is based directly on live fire testing. You can use the SG Calculator for free on the web — you don’t need to download software.
Learn More About SG and BC
 This article is just a brief overview of the interrelated subjects of twist rate, Gyroscopic Stability, and BC. The coverage of twist rates in Modern Advancements in Long-Range Shooting is more detailed, with multiple live fire tests.
This article is just a brief overview of the interrelated subjects of twist rate, Gyroscopic Stability, and BC. The coverage of twist rates in Modern Advancements in Long-Range Shooting is more detailed, with multiple live fire tests.
Other chapters in the book’s twist rate section include:
· Stability and Drag – Supersonic
· Stability and Drag – Transonic
· Spin Rate Decay
· Effect of Twist rate on Precision
Other sections of the book include: Modern Rifles, Scopes, and Bullets as well as Advancements in Predictive Modeling. This book is sold through the Applied Ballistics online store. Modern Advancements in Long Range Shooting is also available in eBook format in the Amazon Kindle store.

















