|
|
January 13th, 2015
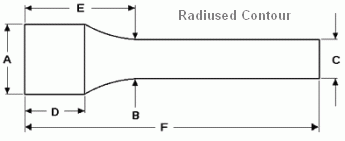
 Are you re-barreling a match rifle and need to know if you will still make weight? Or perhaps you want to select the right contour to hit an optimal carry weight for a new varmint rifle? Dan Lilja offers FREE software that will calculate barrel weight for straight contour, straight taper, and radius-tapered barrels. Dan’s software even calculates how fluting alters barrel weight. Are you re-barreling a match rifle and need to know if you will still make weight? Or perhaps you want to select the right contour to hit an optimal carry weight for a new varmint rifle? Dan Lilja offers FREE software that will calculate barrel weight for straight contour, straight taper, and radius-tapered barrels. Dan’s software even calculates how fluting alters barrel weight.
For general info on barrel weight calculation for straight and straight tapers, read this article on Lilja’s website. Click HERE for another article explaining weight calculation with barrels that have a radiused (curved) contour section.
Here are the free software programs offered by Dan Lilja. Right click and “Save As”:
Straight Contour (.exe file) | Straight Contour (Excel file) | Contoured Barrels with Radius (Excel file)
December 30th, 2014
We can predict, with some certainty, how long a light bulb will last (in use), or a shingle roof, or even a nuclear reactor. But how about barrels? Is there a way to reliably estimate barrel life based on known characteristics? This article explains one effort to quantify barrel life…
 How long will a barrel last before the accuracy “goes south”? There are so many variables involved (powder type, bore diameter, bullet coatings etc.) that it’s hard to predict. You might say “Well, my buddy has a .243 and he got 1500 rounds before the throat was shot out” — those kind of comparisons can be useful, but they’re not very scientific, and they won’t help much if you’ve got a gun in a new chambering (such as the 6.5×47) for which long-term test results are lacking. How long will a barrel last before the accuracy “goes south”? There are so many variables involved (powder type, bore diameter, bullet coatings etc.) that it’s hard to predict. You might say “Well, my buddy has a .243 and he got 1500 rounds before the throat was shot out” — those kind of comparisons can be useful, but they’re not very scientific, and they won’t help much if you’ve got a gun in a new chambering (such as the 6.5×47) for which long-term test results are lacking.
Is there a more reliable way to predict barrel life — one that will work for a broad range of calibers? Well, Forum member MikeCr has developed an Excel spreadsheet that accounts for a number of variables, and gives a pretty good estimate of useful barrel life, whether you’re shooting a .223 Rem or a 338 Lapua Magnum. Mike’s program predicts barrel life using five variables: 1) Bullet Diameter; 2) Powder Charge weight; 3) Powder Heat Potential (KJ/kg); 4) Pressure (in psi); and 5) Bullet Coating (yes/no). Mike provides a table with Heat Potential ratings for most popular powder types. The user needs to know the pressure of his load. This can be estimated with QuickLOAD.
You can download the lastest version of Mike’s spreadsheet below. You’ll need Excel or an Excel viewer to open the file.
Click to Download Spreadsheet: Barrel Life Spreadsheet (Latest Version)
Shown below is Mike’s Spreadsheet, with variables for a 6BR shooting 105gr “naked” bullets with 30.3 grains of Hodgdon Varget powder. The formula predicts 2401 rounds of barrel life. That corresponds pretty well to what we’d expect for a 6BR — about 2500 rounds.
 
Mike observes: “There has been a lot of discussion lately related to cartridge design and resulting barrel life. This is a really important factor to consider amongst a myriad of choices. Barrel life is controversial, and subjective. There are no clear-cut standards for comparison. But a few years ago, I put together a spreadsheet based on Bart Bobbit’s rule of thumb. It worked pretty good, only occasionally failing some tests when validated against posted barrel lives.
According to Ken Howell, I had to account for pressure. And Henry Child’s powder temperature testing provided another piece needed. So, I’ve tweaked it here and there to pass more tests. From 223 Rem to 300 UltraMagnum. Another element added, but turned off, is shot interval. I would need way more tests to lock in on this. But everyone knows, the faster you shoot, the worse the barrel life.
Anyway, another factor hard to define is ‘accurate’ barrel life. This cannot be quantified without standards. Barrels are replaced when expectations are no longer met. I feel that a [barrel] passes peak potential in a finite period due to throat erosion. But that don’t mean it’s toast, if it still shoots well enough. It’s just as likely that many of us never see that peak potential anyway. It’s a slippery thing. Point-blank BR competitors will toss a barrel when it leaves the 1s. I could get another 4000 rounds from it, and be content with its performance, I’m sure.”
NOTE: Mike says: “This spreadsheet may show a lower barrel life than you prefer. But it pretty well spotlights cartridges to stay away from if you plan much time at the range or in dog town.”
Editor’s Comment: Mike’s spreadsheet is a helpful tool, but it is NOT a definitive “take-it-to-the-bank” indicator of barrel life. Mike cautions that predicting barrel life involves so many different factors (including how hot the barrel is run), that the task is a bit like predicting tread life on car tires. Still, the spreadsheet is very helpful. It can certainly warn us that some chamberings (such as the 6-284) are likely to be barrel burners. That can help you make a smart decision when choosing a chambering for your next rifle.
December 25th, 2014
What do you get when you combine red Cerakote and barrel fluting? Well, a candy-cane AR barrel — just in time for the holidays. This unique barrel was created by Black Hole Weaponry in St. Helens Oregon. No this is not a Photoshop job. This barrel is really finished this way (as you can see in the close-up). Thanks to Anette Wachter, aka 30 Cal Gal, for finding this festive firearm fitting.


December 15th, 2014
The U.S. Patent Office has awarded BoreSmith utility patents for two unique gun cleaning products. Patents were issued for BoreSmith’s triangular Pyramid Patch™ as well as BoreSmith’s dual-diameter JagBrush™. Both products were designed by Shane Smith, a mathematician/physicist who used his scientific and firearms knowledge to create innovative bore-cleaning products that may well work better than conventional patches and brushes.
BoreSmith’s clever Triangle Patch™ (aka Pyramid Patch) presents more cleaning surface area to the bore wall than does a conventional square or round patch (of equivalent size). At the same time, the unique geometry makes Triangle Patches much less likely to jam in the barrel. This is because the notches in the sides of the triangle allow the patch to sit more uniformly on the jag (without bunching up). The Triangle patch can be used with a standard jag but works best when paired with BoreSmith’s patented dual-diameter JagBrush. Order Triangle Patches HERE.

Triangle Patch Function and Geometry Explained (See 1:18 time-mark):
NOTE: Despite what you may see in this video, you should insert brushes and patches from the chamber end first, using a well-fitting cleaning rod bore guide. With bolt-action rifles, NEVER insert a cleaning rod (with brush or jag) in through the muzzle. This may damage the delicate crown of your barrel.
Patent Awarded to Dual-Diameter JagBrush
The JagBrush is like a standard bore brush but has two different diameters on the bristle section. Bristles in the front are smaller, while the rear bristles are similar length to a standard bore brush. When a patch is pushed through the bore using a JagBrush, the smaller bristles will grab the patch, leaving the longer bristles exposed and creating a dual-action wiping + brushing system. JagBrushes are offered in a wide variety of calibers, in both bronze and nylon versions.


Shane Smith, CEO of BoreSmith, was pleased that his designs have been awarded two important patents: “I created these tools to allow the user to get their firearms cleaner, faster, and without causing unnecessary damage in the process. At BoreSmith, we strive to develop and produce superior cleaning tools that help firearm owners protect their investments.” For more info, visit BoreSmith at RigelProducts.com.
December 8th, 2014
Need a new barrel for your Remington-actioned hunting or tactical rifle? McRee’s Precision has you covered. McRee’s is now offering complete, no-gunsmithing re-barreling kits for Remington and Rem-clone actions. These feature a high-quality, pre-chambered “PRE-FIT” stainless barrel from Criterion, a Savage-style barrel nut, a recoil lug, and a special barrel-nut wrench. With this system you can easily re-barrel your favorite Remington rifle yourself in less than an hour. You don’t need to pay gunsmithing fees, or wait weeks (or months) for a busy smith to do the job.
McRee’s Precision Remington DIY Barrel Kit includes Criterion Pre-Fit Stainless Barrel, Barrel Nut, Recoil Lug, and Barrel Nut Wrench:

CLICK HERE for Barrel Specifications PDF Sheet
Right now McRee’s Precision is offering Rem-action Pre-Fit barrel packages (complete with barrel nut, recoil lug, and wrench) starting at just $412.50 (On Sale). Choose from four chamberings: .243 Win, .260 Rem, .308 Win, and .300 Win Mag. These Pre-Fit barrel kits are “100% complete and ready-to-install”. All you need to do is remove your current barrel, place the recoil lug, spin on the new tube, follow the instructions for setting head-space, then torque the barrel nut against the lug. NOTE: You may require a barrel vise and action wrench to remove the original barrel. Minor inletting changes may be needed forward of the action.

The folks at McRee’s Precision say their Pre-Fit system offers many advantages: “Remington Pre-Fitted Barrel Kits have become popular over the years. If Savage can do it, why not for our Remingtons? Our [Criterion-supplied] barrels are spec’d to the McRee standard of performance. We require a minimum of 0.5 MOA with good factory ammo and 0.2 MOA with quality handloads. There are several places to get the tools required to remove your factory barrel correctly. Once you have your barrel removed all you have to do is follow the normal Savage procedure to install your new barrel. We recommend that you contact your local gunsmith for the install. Feel free to call us with any questions.”
Product Tip from Ed LongRange. We welcome readers’ submissions.
December 6th, 2014
Next time you have a barrel fitted, consider having your gunsmith create a “stub gauge” from a left-over piece of barrel steel (ideally taken from your new barrel blank). The outside diameter isn’t important — the key thing is that the stub gauge is created with the same reamer used to chamber your current barrel, and the stub must have the same bore diameter, with the same land/groove configuration, as the barrel on your rifle. When properly made, a stub gauge gives you an accurate three-dimensional model of the upper section of your chamber and throat. This comes in handy when you need to bump your case shoulders. Just slide a fired case (with spent primer removed) in the stub gauge and measure from base of case to the end of the gauge. Then, after bumping, re-measure to confirm how much you’ve moved the shoulder.
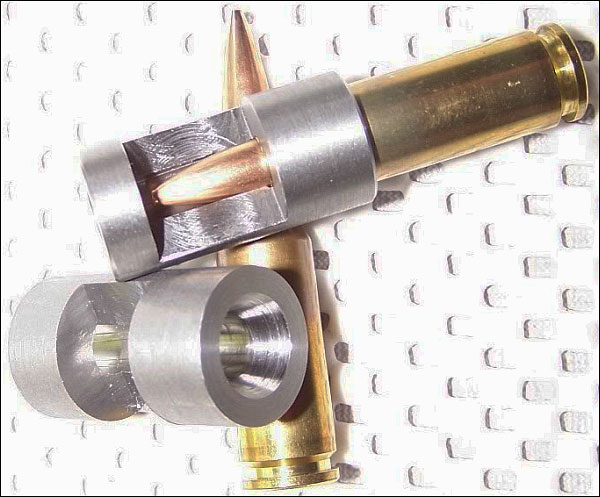

In addition, the stub gauge lets you measure the original length to lands and freebore when your barrel was new. This gives you a baseline to accurately assess how far your throat erodes with use. Of course, as the throat wears, to get true length-to-lands dimension, you need take your measurement using your actual barrel. The barrel stub gauge helps you set the initial bullet seating depth. Seating depth is then adjusted accordingly, based on observed throat erosion, or your preferred seating depth.
Forum member RussT explains: “My gunsmith [makes a stub gauge] for me on every barrel now. I order a barrel an inch longer and that gives him enough material when he cuts off the end to give me a nice case gauge. Though I don’t have him cut that nice-looking window in the side (as shown in photos). That’s a neat option. You can tell how much throat erosion you are getting from when it was new as well. For measuring initial seating depths, this is the most useful item on my loading bench next to calipers. Everyone should have a case gauge made by there smith if you have a new barrel put on.”
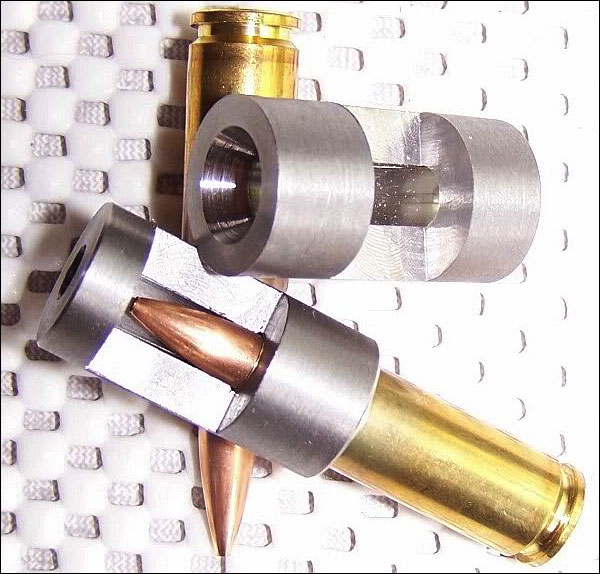
Forum member Lawrence H. has stub gauges made with his chamber reamers for each new barrel. He has his smith cut a port in the stub steel so Lawrence can actually see how the bullet engages the rifling in a newly-cut chamber. With this “view port”, one can also see how the case-neck fits in the chamber. Lawrence tells us: “My stub gauges are made from my barrels and cut with my chamber reamers. With them I can measure where my bullets are ‘touching the lands’ and shoulder bump dimensions. This is a very simple tool that provides accurate information.” To learn more about stub gauges, read this Forum Thread. The photos above and below show Lawrence’s stub gauges:

November 10th, 2014
A Negligent Shooter Gets Lucky
Here we have a story so filled with negligent acts that I can only marvel that the shooter survived the experience. The photo and narrative were provided by the gunsmith who took in the repair job, my comments are in italics. It’s worth reading, we can’t get enough safety warnings in our hobby. — GS Arizona, Riflemans Journal
Below is a sectioned barrel showing an 80gr Sierra that was fired in a .223 bolt action with a cleaning rod in the bore. Both the bullet and the rod are still in the bore.

This article originally appeared in the Riflemans Journal website.
Description of Incident (with Commentary)
The shooter had a stuck case in his .223 chamber. The stuck case was actually a loaded round that didn’t fire. It wouldn’t extract because it was a .222 case that got mixed in with his .223 brass. [He had loaded the wrong brass.] I saw the loaded round with an 80gr bullet in it and a light primer strike. Negligent Act #1: Wrong brass was mixed in with the brass being reloaded.
The shooter removed the stuck case with a 3-piece aluminum rod. Negligent Act #2: Hammering out a loaded round with a cleaning rod. People have been killed doing this as the round can fire and drive the cleaning rod right into you. I remember one such incident about 5 years ago, the shooter was pounding out a stuck round, the cleaning rod went right through him, he didn’t survive.
The shooter didn’t notice only two segments of the cleaning rod came out when he removed it. Negligent Act #3: If you put anything at all down the barrel of a rifle you’d better make darn sure you got it all out before doing anything else!
He then chambered another round and fired it. Negligent act #4: If you’ve had a barrel obstruction of any kind, and if you’ve put something in the barrel, look through the barrel before proceeding! Within the past two years I know of an incident in which a benchrest shooter was killed in exactly this manner. The pressure built up and the rifle bolt came out of the receiver and into his chest.
The shooter is ‘OK’, but did not escape unscathed. He said there was a huge explosion and after regaining his senses found he was bleeding heavily from his forehead. The blood was thick enough that it ran in his eyes and he couldn’t see. In his words “I thought I was going to die”.
He has what looks like a pretty deep cut about an inch long on the side of his head, right in line with his right eye starting where the eye socket turns out to the side of the skull. And no telling what he’s got in the way of brass particles embedded in his forehead.
He was shooting on private property, and was alone when this happened. Negligent Act #5: Don’t shoot alone! Accidents happen, this is just one more example. If we could predict accidents, we wouldn’t have them. Always shoot with at least one other person.
He managed to get the bleeding stopped, or at least under control, packed his car and drove himself home without seeking immediate medical attention. Negligent Act #6: This one could have cost him his life after being lucky enough to survive the incident. There’s no way to know what’s happened just after an incident like this. He should have been at a hospital getting checked for shrapnel in the head.
The rod and slug could not be driven out. Since the barrel had a high round count there was no point in trying to salvage it. Note that the aluminum rod is expanded to a tight fit in the bore for the first couple inches. The base of the bullet is a little over 2″ from the mouth of the chamber.
What we’ve seen here is negligence and an absolute indifference to the established rules of safe reloading and gun handling, from start to finish, capped off with the shooter’s foolish avoidance of medical treatment. This shooter is lucky to be alive, but he’s surely used up all his luck. Don’t assume you’ll be so fortunate.
October 30th, 2014
Can sustained rapid-fire shooting with no cool-down period wear out a quality barrel more quickly? The answer is “Yes” according to Forum member LCazador, who recently did an interesting comparison test with two .243 Win barrels. He started off with two, identical, match-grade HV taper stainless barrels. Both were NEW at the start of testing, and LCazador shot the same load through each: 95gr match bullets with 38 grains of Hodgdon Varget. After giving both barrels the same, gentle 20-round break-in, 300 rounds were then fired through each barrel — in very different ways. Barrel condition and wear were monitored with a borescope.
Barrel One — Slow Fire, Cool Down Periods, Cleaning Every 50 Rounds
At the end of the 300-round test, Barrel One looked brand new. There was none of the severe fire cracking found in Barrel Two. This barrel was shot no more than 10 times without a cool down and firing was done at a much slower pace. Cleaning for this barrel was done every 50 shots.
Barrel Two — Fast Firing, No Waiting, Cleaning Every 100 Rounds
The second barrel, which received hard use and minimal cleaning, was severely damaged with severe fire cracking at the leade and throat. As a result, the barrel had to be re-chambered. This barrel was shot 100 rounds at time without cleaning and was shot up to 20 times in succession without a cool down.
Don’t let your barrel get too hot, and keep it clean. One afternoon can ruin a barrel!
 Monitoring Barrel Wear with Borescope Monitoring Barrel Wear with Borescope
Some folks worry too much about what their borescopes reveal — many barrels do not have to be “squeaky clean” to perform well. In fact some barrels run better after ten or more fouling shots. However, a borescope can be very helpful when your barrel starts losing accuracy for no apparent reason. Forum member FdShuster writes:
“A borescope is a positive way of backing up your suspicions when the rifle starts to throw an occasional (soon followed by more frequent) wild shot. Using the scope is also an excellent way to determine that the cause is barrel wear and not simply a need for a concentrated cleaning session to remove built up copper and more importantly, carbon fouling.
I’ve had a few barrels that gave every indication of being shot out. But I ‘scoped them out and found the cause to be nothing more than requiring a good cleaning. They then returned to their usual performance. There’s no guessing involved when you are able to get ‘up close and personal’ using the scope. The borescope also provides an excellent view of the all-important condition of the crown. My borescope is one of the most valuable investments I’ve ever made.”
October 10th, 2014
Do you think your borescope is a state-of-the-art bore inspection device? Well think again. There is now something way more advanced than any optical borescope. A new laser-equipped scanning device can map the entire interior surface of a barrel bore. With this new technology you can now examine every land and every groove, millimeter by millimeter, from the chamber to the tip of the muzzle. The most minute flaw in a barrel can now be revealed.
 The new device is called the BEMIS-SC™ (for Barrel Inspection Machine Small Caliber). Operated by Chesapeake Testing and Laser Techniques Company (LTC), BEMIS-SC performs non-destructive laser-based mapping of gun bores. The BEMIS-SC currently works with .22 caliber to .50 caliber (5.56 – 12.7 mm) barrels. The BEMIS captures thousands of highly accurate data points over the full length of a barrel. The inspection can be completed in mere minutes, with scan results displayed in graphical, tabular, and 3D visual formats. Here is a barrel cross-section, as scanned by the BEMIS-SC: The new device is called the BEMIS-SC™ (for Barrel Inspection Machine Small Caliber). Operated by Chesapeake Testing and Laser Techniques Company (LTC), BEMIS-SC performs non-destructive laser-based mapping of gun bores. The BEMIS-SC currently works with .22 caliber to .50 caliber (5.56 – 12.7 mm) barrels. The BEMIS captures thousands of highly accurate data points over the full length of a barrel. The inspection can be completed in mere minutes, with scan results displayed in graphical, tabular, and 3D visual formats. Here is a barrel cross-section, as scanned by the BEMIS-SC:
Click for Full-Screen Version

Until the 1980s, gun tube inspection had to be conducted by hand using a manual “star” gauge, a process that would take hours and provide minimal data. Electronic gauges were eventually developed along with the video bore scope, but these systems were still limited to very few, low-resolution data points. That has all changed with the BEMIS™, a huge leap forward in technology that is capable of rapidly capturing thousands of precise data points.
BEMIS-SC (Small Caliber) Barrel Inspection Machines

Chesapeake Testing commenced BEMIS-SC barrel inspection services in September 2014. Testing is performed in Chesapeake’s commercial barrel inspection laboratory, located in Belcamp, MD, minutes from the U.S. Army Aberdeen Proving Ground. While testing is currently limited to .22 to .50 caliber barrels, Chesapeake Testing will accommodate both smaller and larger calibers in the future.
“We have always focused on building our company around very unique technologies. BEMIS™ has changed the industry in regards to the inspection of weapon systems. We are excited to be an exclusive partner with LTC in this industry and look forward to contributing to the future of this technology,” says Jim Foulk, founder and president of Chesapeake Testing.
September 20th, 2014
Put the same load in a variety of barrels (with the same length and chamberings) and you’ll see a wide variance in muzzle velocity. In fact, it’s not unusual to see up to 100 fps difference from one barrel to the next. We demonstrated this with a comparison test of Lapua factory ammo.
Chron Testing Lapua Factory Ammo
At our Southern California test range, we chronographed Lapua 105gr 6mmBR factory ammo in three different 8-twist barrels of similar length. The results were fascinating. Lapua specs this ammo at 2790 fps, based on Lapua’s testing with its own 26″ test barrel. We observed a speed variance of 67 fps based on tests with three aftermarket barrels.

Brand ‘S’ and Brand ‘PN’ were pre-fit barrels shot on Savage actions. Brand ‘K’ was fitted to a custom action. All test barrels were throated for the 100-108 grain bullets, though there may have been some slight variances in barrel freebore. With a COAL of 2.330″, the rounds were “jumping” to the rifling in all barrels. Among the four barrels, Brand ‘PN’ was the fastest at 2824 fps average — 67 fps faster than the slowest barrel. Roughly 10 fps can be attributed to the slightly longer length (27″ vs. 26″), but otherwise this particular barrel was simply faster than the rest. (Click Here for results of 6mmBR Barrel Length Velocity Test).
Results Are Barrel-Specific, Not Brand-Specific
These tests demonstrate that the exact same load can perform very differently in different barrels. We aren’t publishing the barrel-makers’ names, because it would be wrong to assume that ‘Brand X’ is always going to be faster than ‘Brand Y’ based on test results from a single barrel. In fact, velocities can vary up to 100 fps with two identical-spec barrels from the SAME manufacturer. That’s right, you can have two 8-twist, 26″ barrels, with the same land-groove configuration and contour, from the same manufacturer, and one can be much faster than another.
Don’t Demand More Than Your Barrel Can Deliver
We often hear guys lament, “I don’t get it… how can you guys get 2900 fps with your 6BRs and I can only get 2840?” The answer may simply be that the barrel is slower than average. If you have a slow barrel, you can try using more powder, but there is a good chance it may never run as fast as an inherently fast barrel. You shouldn’t knock yourself out (and over-stress your brass) trying to duplicate the velocities someone else may be getting. You need to work within the limits of your barrel.
Factory Ammo Provides a Benchmark
 If you have a .223 Rem, 6BR, .243 Win, 6.5×47 Lapua, 6.5×55, .308 Win, 30-06, or 300 WM Rifle, we recommend you buy a box of Lapua factory-loaded ammo. This stuff will shoot great (typically around half-MOA), and it can give you a baseline to determine how your barrel stacks up speedwise. When you complete a new 6BR rifle, it’s wise to get a box of the factory ammo and chronograph it. That will immediately give you a good idea whether you have a slow, average, or fast barrel. Then you can set your velocity goals accordingly. For example, if the factory 6BR ammo runs about 2780-2790 fps in your gun, it has an average barrel. If it runs 2820+ in a 26″ barrel (or 2835 fps in a 28″), you’ve got a fast tube. If you have a .223 Rem, 6BR, .243 Win, 6.5×47 Lapua, 6.5×55, .308 Win, 30-06, or 300 WM Rifle, we recommend you buy a box of Lapua factory-loaded ammo. This stuff will shoot great (typically around half-MOA), and it can give you a baseline to determine how your barrel stacks up speedwise. When you complete a new 6BR rifle, it’s wise to get a box of the factory ammo and chronograph it. That will immediately give you a good idea whether you have a slow, average, or fast barrel. Then you can set your velocity goals accordingly. For example, if the factory 6BR ammo runs about 2780-2790 fps in your gun, it has an average barrel. If it runs 2820+ in a 26″ barrel (or 2835 fps in a 28″), you’ve got a fast tube.

|
 Are you re-barreling a match rifle and need to know if you will still make weight? Or perhaps you want to select the right contour to hit an optimal carry weight for a new varmint rifle? Dan Lilja offers FREE software that will calculate barrel weight for straight contour, straight taper, and radius-tapered barrels. Dan’s software even calculates how fluting alters barrel weight.
Are you re-barreling a match rifle and need to know if you will still make weight? Or perhaps you want to select the right contour to hit an optimal carry weight for a new varmint rifle? Dan Lilja offers FREE software that will calculate barrel weight for straight contour, straight taper, and radius-tapered barrels. Dan’s software even calculates how fluting alters barrel weight.












 How long will a barrel last before the accuracy “goes south”? There are so many variables involved (powder type, bore diameter, bullet coatings etc.) that it’s hard to predict. You might say “Well, my buddy has a .243 and he got 1500 rounds before the throat was shot out” — those kind of comparisons can be useful, but they’re not very scientific, and they won’t help much if you’ve got a gun in a new chambering (such as the 6.5×47) for which long-term test results are lacking.
How long will a barrel last before the accuracy “goes south”? There are so many variables involved (powder type, bore diameter, bullet coatings etc.) that it’s hard to predict. You might say “Well, my buddy has a .243 and he got 1500 rounds before the throat was shot out” — those kind of comparisons can be useful, but they’re not very scientific, and they won’t help much if you’ve got a gun in a new chambering (such as the 6.5×47) for which long-term test results are lacking.











 Monitoring Barrel Wear with Borescope
Monitoring Barrel Wear with Borescope The new device is called the BEMIS-SC™ (for Barrel Inspection Machine Small Caliber). Operated by
The new device is called the BEMIS-SC™ (for Barrel Inspection Machine Small Caliber). Operated by 


 If you have a .223 Rem, 6BR, .243 Win, 6.5×47 Lapua, 6.5×55, .308 Win, 30-06, or 300 WM Rifle, we recommend you buy a box of
If you have a .223 Rem, 6BR, .243 Win, 6.5×47 Lapua, 6.5×55, .308 Win, 30-06, or 300 WM Rifle, we recommend you buy a box of 





