|
|
August 3rd, 2014
Need something for the walls of your “man cave” or reloading room? Check out these jumbo-size cartridge posters. The creators of the Cartridge Comparison Guide now offer three very large full-color printed posters. These can be tacked to a wall or matted/framed to hang like paintings. Three different posters are available.
Rifleman’s Classic Poster (38″ x 27″)
The Rifleman’s Classic Poster, a full 38 inches wide and 27 inches tall, is the most comprehensive. This $19.95 poster displays 272 rifle cartridge types at true size (within 4/1000 of an inch). Cartridges shown range from .17 caliber all the way up to the big boomers (including some cannon shells). The Rifleman’s Classic poster includes all American Standardized Rifle Cartridges (as of 2013) and many European rifle cartridges. The poster is a good representation of military cartridges dating back to WWI and includes cartridges such as the 13X92mm MSR and the .55 Boys.
CLICK Image to Enlarge:

American Standard Cartridge Poster (Rifle, Handgun, Shotgun) — $15.95
The 36″ x 24″ American Standard Poster displays 165 rifle cartridges, 55 handgun cartridges, and 9 different shotgun gauges. This includes all American Standardized Cartridges (rifle, handgun, and shotgun) available as of January 2012. All cartridge types are displayed in full color, actual size. The rifle selection includes all standard hunting cartridges from the 17 Mach 2 through the .505 Gibbs and .577 Nitro. Bonus cartridges include the .375 and .408 Chey-Tac, .416 Barrett, .50 BMG, 50-20 and 20mm. The Handgun section covers cartridges from the 17 HMR to the 500 S&W. Shotgun cartridges include the .410 and 32 gauge up to the 8 gauge. NOTE: Wildcat, proprietary, and obsolete-historic cartridges are NOT included in this poster.
CLICK Image to Enlarge:

BIG BORE Cartridge Poster (215 Cartridges) — $15.95
The 36″ x 24″ Big Bore Poster illustrates over 215 large=caliber rifle cartridges, all shown actual size in full color. These include Standard, Historic, Military, Proprietary and Wildcat rifle cartridges side by side. Cartridges illustrated range from the subsonic .338 Spectre up to the monstrous .729 Jongmans. The poster also includes historically significant cartridges such as the 12 Gauge Paradox, 4 Bore, 1″ Nordfelt, 50 BAT Spotter, .50 BMG, .5 Vickers, 12.7×108 Russian, 20mm, 25mm, 30mm and more.
CLICK Image to Enlarge:

April 6th, 2014
As a cartridge case is reloaded multiple times, burnt powder residue and carbon builds up on the inside of the case. Unless the case interior is cleaned in some fashion, eventually you’ll see a reduction in case capacity. One of our Forum members from Australia wonders about the effects of reduced case capacity: “If the capacity of the case decreases as the crud builds up, then it effectively reduces the chamber size. Wouldn’t that change the pressure produced from that of an equivalent clean case?”
Ultrasonic Cleaning Example:

Interesting Test of Case Capacity Changes
Forum member Fred Bohl has actual test results that can help answer the above question. Fred proved that, over a 20-reload cycle, the case capacity of uncleaned cases did, indeed, decline a small amount. However, surprisingly, this did not seem to affect the actual chronographed velocity of the load. ES did increase, but Fred believes the higher ES was due to changes in case-neck tension, rather than due to the slight reduction in case capacity.
Fred reports: “Back when beginning to use ultrasonic case cleaning, part of the motivation was to get the inside clean based on the assumption that allowing burnt residue to build up inside cases would affect capacity, and, ultimately, performance. An experiment was done to test this hypothesis. The load used, 30.5 grains of RL15 behind 107gr SMKs in a 6mmBR, was selected for best group and lowest ES in prior load development. It turned out to be 92% of initial case capacity and neither “full” or compressed. (I would suspect that different powders, load weight, and total case capacity might produce very different results.)
We took 30 cases of identical initial capacity and tracked three lots of 10 each:
LOT 1: No Internal cleaning
LOT 2: Cleaned with media in tumbler
LOT 3: Cleaned with Ultrasound machine
Each case (in each lot) was shot and reloaded 20 times. The simplified results after 20 reloads of each lot were as follows:
Lot 1 (not cleaned) – 0.3 to 0.4 gr. loss of capacity, 5 to 8 fps greater ES.
Lot 2 (tumble cleaned) – 0.1 to 0.3 gr. loss of capacity, 4 to 6 fps greater ES.
Lot 1 (ultrasonic cleaned) – no loss of capacity, no detectable change in ES.
FINDINGS
There was no detectable correlation of velocity change to the lots. An oddity was that on very hot days Lot 1 velocities were, occasionally, slightly higher. [Editor’s note: That does suggest that the carbon build-up inside the uncleaned cases might cause a slight increase in pressure that shows up on hot days. Fred has posted that “A local shooter reported doing the 20 reload, no clean test on a .308 that gave a loss of capacity of 2.0 grains, doubled ES and signficant velocity changes. However, I don’t have any details on his load weight or powder.”]
NOTE: From results of another ongoing test, I believe the above differences in ES are probably due more to variance in bullet grip tension than case capacity. The ultrasound cleaned cases (LOT 3) did maintain the lowest ES, but we are not 100% sure of the reasons why. More consistent bullet seating might be the reason.
[Editor’s comment: Jason found that with his ultrasonically-cleaned cases, the inside of the necks got so “squeaky clean” that he needed to use dry lube in the necks. Jason uses the $10.95 dry lube kit from Neconos.com. This applies ultra-fine Moly powder to the neck using small carbon steel balls]

March 25th, 2014
The “Old Warhorse” .30-06 Springfield cartridge is not dead. That’s the conclusion of Forum member Rick M., who recently compared the 1000-yard performance of his .30-06 rifle with that of a rig chambered for the more modern, mid-sized 6.4×47 Lapua cartridge. In 12-16 mph full-value winds, the “inefficient and antiquated” .30-06 ruled. Rick reports:
“I was shooting my .30-06 this past Sunday afternoon from 1000 yards. The wind was hitting 12-16 mph with a steady 9 O’clock (full value) wind direction. My shooting buddy Jeff was shooting his 6.5×47 Lapua with 123gr Scenar bullets pushed by Varget. Jeff needed 13 MOA left windage to keep his 6.5x47L rounds inside the Palma 10 Ring. By contrast I only needed 11.5 MOA left windage with my .30-06. I was shooting my ’06 using the 185gr Berger VLD target bullet with H4350. I managed the same POI yet the .30-caliber bullet only needed 11.5 MOA windage. That’s significant. From this experience I’ve concluded that the Old Warhorse ain’t quite dead yet!”


Rick likes his “outdated” .30-06 rifle. He says it can deliver surprisingly good performance at long range:
“To many of the younger generation, the Old Warhorse .30-06 is ‘outdated’ but I can guarantee that the .30-06 Springfield is a VERY ACCURATE cartridge for 1000-yard shooting (and even out further if need be). With some of the advanced powders that we have today, the .30-06 will surprise many shooters with what it’s capable of doing in a good rifle with the right rate of twist. My rifle has a 1:10″ twist rate and I had it short-throated so that, as the throat erodes with time, I could just seat the bullets out further and keep right on shooting. My recent load is Berger 185gr Target VLDs pushed by IMR 4350. This is a very accurate load that moves this bullet along at 2825 fps.”

March 20th, 2014
This new tool trims cases quickly, with precision control over case length via a micrometer-type dial. The folks at ACT Tactical have developed an easy-to-use compact case trimmer called the TRIM-IT. Crafted from 6061-T6 aluminum, this sturdy case trimmer comes with a 100% lifetime guarantee. The $97.50 TRIM-IT features a micrometer that’s built into the unit itself. Caliber-specific inserts (called “Caliber Dies”) index off the case shoulder.

The TRIM-IT can work with any hand-drill or drill press. Once you get the hang of it, you can trim a case in 7-8 seconds — that gives you a production rate of 400+ cases per hour. The TRIM-IT delivers repeatable precision to plus/minus one-thousandth. This unit also holds its cut-length setting, unlike some other trimmers which require frequent adjustment.

The basic unit ships with two caliber dies, for .223 and .308. Other listed caliber dies include 6.8 SPC, .300 BLK, .30-06, 30-30 Win, 300 Win Mag, 7MM REM, 7.62x54R, and 8MM Mauser. Other cartridge types can be custom-ordered from EZTrimit.com. To change dies, simply loosen the set screw on the TRIM-IT, take the caliber die out, add another one, and tighten the screw — quick and easy.
The built-in micrometer is great. The handy dial gives you a positive, repeatable length setting quickly — no fiddling with locking rings or spacers. Once you get the ring set properly, the cut lengths are consistent from the first case to the last. Expect your case OAL spread to be about +/- .001″ (starting with full-length-sized cases with uniform rim to shoulder lengths). For more information, email sales [at] eztrimit.com or call (562) 602-0080. You can see how the Trim-It device works in the video below.
Video Shows Trim-it Set-Up and Operation
March 2nd, 2014
What is “Overbore”? That’s a question rifle shooters can debate to no end. This article from our archives proposes one way to identify “overbore cartridges”. We think the approach outlined here is quite useful, but we know that there are other ways to define cartridges with “overbore” properties. Whenever we run this article, it stimulates a healthy debate among our readers — and that is probably a good thing.
Forum Member John L. has been intrigued by the question of “overbore” cartridges. People generally agree that overbore designs can be “barrel burners”, but is there a way to predict barrel life based on how radically a case is “overbore”? John notes that there is no generally accepted definition of “overbore”. Based on analyses of a wide variety of cartridges, John hoped to create a comparative index to determine whether a cartridge is more or less “overbore”. This, in turn, might help us predict barrel life and maybe even predict the cartridge’s accuracy potential.
John tells us: “I have read countless discussions about overbore cartridges for years. There seemed to be some widely accepted, general rules of thumb as to what makes a case ‘overbore’. In the simplest terms, a very big case pushing a relatively small diameter bullet is acknowledged as the classic overbore design. But it’s not just large powder capacity that creates an overbore situation — it is the relationship between powder capacity and barrel bore diameter. Looking at those two factors, we can express the ‘Overbore Index’ as a mathematical formula — the case capacity in grains of water divided by the area (in square inches) of the bore cross-section. This gives us an Index which lets us compare various cartridge designs.”


OVERBORE INDEX Chart
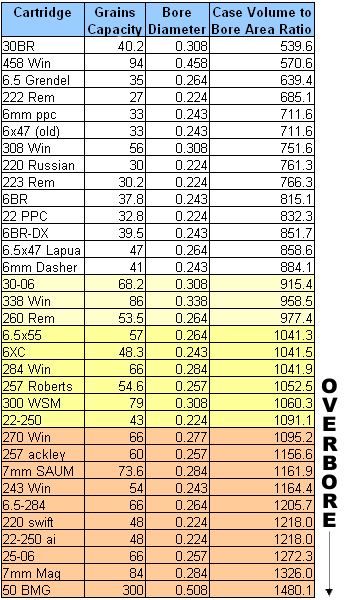
So what do these numbers mean? John says: “My own conclusion from much reading and analysis is that cartridges with case volume to bore area ratio less than 900 are most likely easy on barrels and those greater than 1000 are hard on barrels.” John acknowledges, however, that these numbers are just for comparison purposes. One can’t simply use the Index number, by itself, to predict barrel life. For example, one cannot conclude that a 600 Index number cartridge will necessarily give twice the barrel life of a 1200 Index cartridge. However, John says, a lower index number “seems to be a good predictor of barrel life”.
John’s system, while not perfect, does give us a benchmark to compare various cartridge designs. If, for example, you’re trying to decide between a 6.5-284 and a 260 Remington, it makes sense to compare the “Overbore Index” number for both cartridges. Then, of course, you have to consider other factors such as powder type, pressure, velocity, bullet weight, and barrel hardness.
Overbore Cases and Accuracy
Barrel life may not be the only thing predicted by the ratio of powder capacity to bore cross-section area. John thinks that if we look at our most accurate cartridges, such as the 6 PPC, and 30 BR, there’s some indication that lower Index numbers are associated with greater inherent accuracy. This is only a theory. John notes: “While I do not have the facilities to validate the hypothesis that the case capacity to bore area ratio is a good predictor of accuracy — along with other well-known factors — it seems to be one important factor.”
February 15th, 2014
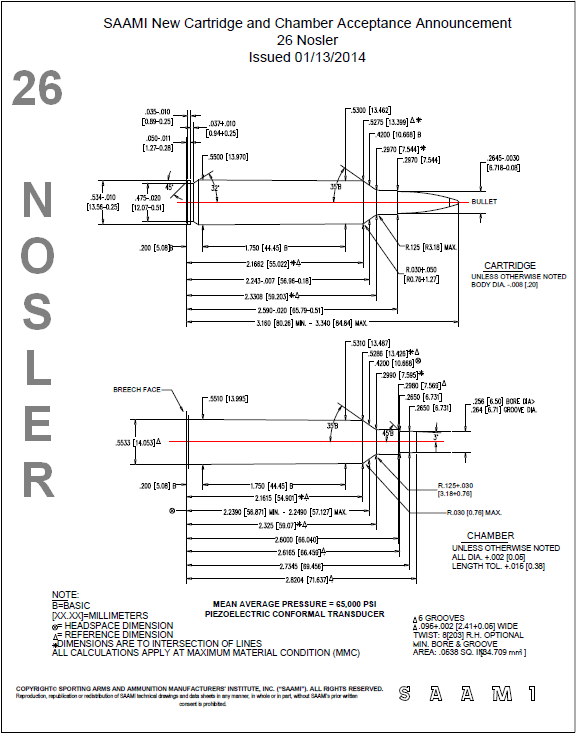
 Nosler has introduced a new 6.5mm (.264 caliber) hunting cartridge, the 26 Nosler. Nosler will initially offer 26 Nosler cartridge brass, and then, eventually, 26 Nosler loaded ammunition. Nosler has introduced a new 6.5mm (.264 caliber) hunting cartridge, the 26 Nosler. Nosler will initially offer 26 Nosler cartridge brass, and then, eventually, 26 Nosler loaded ammunition.
This new cartridge is designed to be a speedy, flat-shooting hunting cartridge, with performance exceeding a 6.5-284. This is possible because the 26 Nosler is a big, long cartridge with plenty of “boiler room”. Length from base to neck/shoulder junction is 2.33″ for the 26 Nosler, compared to 1.91″ for the 6.5-284 (and 2.04″ for a 7mm Rem Magnum). The 26 Nosler has a 35° shoulder angle and a magnum-size 0.534″ outside rim diameter.
The 26 Nosler cartridge can drive the Nosler 129 grain, AccuBond® LR bullet at 3400 fps. Zeroed at 350 yards, the 26 Nosler has a Point Blank Range of 0-415 yards. Loaded with the 129gr Accubond, the 26 Nosler retains as much velocity at 400 yards as a .260 Rem produces at the muzzle. This makes the 26 Nosler a “quintessential deer, antelope and long-range” cartridge according to company CEO/President Bob Nosler.
Nosler has just released the SAMMI print for this cartridge. CLICK HERE for SAMMI Print PDF.
 Credit Grant G. for story tip. We welcome reader submissions.
Credit Grant G. for story tip. We welcome reader submissions.
February 1st, 2014
 Content of all kinds is going digital, and that includes Reloading manuals. Now Hornady is offering an eBook version of the Hornady Handbook of Cartridge Reloading (9th Edition). Priced at $18.99, the eBook version of the Hornady Reloading Manual is now available for iOS (Apple) devices, for Android devices, and for Kindle eReaders. Content of all kinds is going digital, and that includes Reloading manuals. Now Hornady is offering an eBook version of the Hornady Handbook of Cartridge Reloading (9th Edition). Priced at $18.99, the eBook version of the Hornady Reloading Manual is now available for iOS (Apple) devices, for Android devices, and for Kindle eReaders.
For Apple products such iPads and iPhones etc., you can source Hornady’s manual from the iTunes iBook store. For Android tablets and Kindle readers, you can get the Kindle edition from Amazon.com. (NOTE: Android users must install a free Kindle App.)
Hornady’s latest Handbook of Cartridge Reloading features over 900 pages of information, including much new data for the 9th Edition. For many cartridge types, load recipes for new propellants such as Power Pro Varmint, AR-Comp, and CFE-223 have been added in the 9th Edition. Cartridge additions include the 17 Hornet, .327 Federal, .356 Winchester, .416 Barrett and .505 Gibbs. You’ll also find expanded data on over 20 favorite cartridges including: .223 Rem, 300 Whisper/AAC Blackout, .308 Win, .25-06, .257 Wby Mag, and many more. And of course the load recipes provide cover popular Hornady bullets V-MAX, SST, InterBond, InterLock, A-MAX, XTP, NTX and more. Each cartridge write-up features applicable Hornady bullets along with velocity/powder charts for quick and easy reference.
In addition to the comprehensive reloading charts, this reference manual provides helpful explanations of internal, external and terminal ballistics. To learn more about the eBook versions of Hornady’s latest Reloading manual, visit iTunes or Amazon.com.
eBook Tip from EdLongrange. We welcome reader submissions.
December 19th, 2013
 On his Riflemans’ Journal blog, German Salazar wrote an excellent article about cartridge Case-Head Separation. We strongly recommend that you read this article. German examines the causes of this serious problem and he explains the ways you can inspect your brass to minimize the risk of a case-head separation. As cases get fired multiple times and then resized during reloading, the cases can stretch. Typically, there is a point in the lower section of the case where the case-walls thin out. This is your “danger zone” and you need to watch for tell-tale signs of weakening. On his Riflemans’ Journal blog, German Salazar wrote an excellent article about cartridge Case-Head Separation. We strongly recommend that you read this article. German examines the causes of this serious problem and he explains the ways you can inspect your brass to minimize the risk of a case-head separation. As cases get fired multiple times and then resized during reloading, the cases can stretch. Typically, there is a point in the lower section of the case where the case-walls thin out. This is your “danger zone” and you need to watch for tell-tale signs of weakening.
The photo below shows a case sectioned so that you can see where the case wall becomes thinner near the web. German scribed a little arrow into the soot inside the case pointing to the thinned area. This case hadn’t split yet, but it most likely would do so after one or two more firings.

One great tip offered by German Salazar involves using a bent paper clip to detect potential case wall problems. Slide the paper clip inside your case to check for thin spots. German explains: “This simple little tool (bent paper clip) will let you check the inside of cases before you reload them. The thin spot will be immediately apparent as you run the clip up the inside of the case. If you’re seeing a shiny line on the outside and the clip is really hitting a thin spot inside, it’s time to retire the case. If you do this every time you reload, on at least 15% of your cases, you’ll develop a good feel for what the thin spot feels like and how it gets worse as the case is reloaded more times. And if you’re loading the night before a match and feel pressured for time — don’t skip this step!”

December 19th, 2013
Since 2010, Lapua has shipped its quality cartridge brass in sturdy blue plastic boxes. Here’s a handy tip for you — don’t toss the plastic boxes when you load up your brass! These are double-duty containers. If you’re not familiar with “Blue Box” Lapua brass, you may not realize that the boxes are designed to serve as 50-round carriers for your loaded ammo and fired cases. (Yes we know some folks who’ve been tossing out their blue boxes without knowing how the boxes work as caddies.)
Snapped in place under the box lid is a rectangular plastic grid that fits in the bottom of the box. Pop the grid loose and slide it into the box with the smooth side facing up. Side supports molded into the lower section hold the grid in place.

Voilà, instant Ammo Box! Each grid contains holes for fifty (50) loaded rounds or empty cases. The convertible plastic container/ammo box is a great idea that Lapua executed very nicely. Now you have even more motivation to purchase your cartridge brass from Lapua.

December 14th, 2013
Lapua just dropped a bombshell — multiple bombshells, in fact. Lapua just announced that it will be producing .221 Fireball brass and .50 BMG brass starting early 2014. This will be the first truly match-grade brass ever offered for the .221 Fireball. That’s great news for varminters, who can use Lapua’s new .221 Fireball brass “as is” or neck it down to .20 Vartarg or 17 Fireball. Tactical shooters can also use the .221 Fireball brass to make the .300 Whisper and 300 Blackout sub-sonic cartridges. At the other end of the spectrum, ultra-long-range shooters now have a new ultra-premium brass source for the mighty .50 BMG. This is potentially a “game-changer” for fifty-cal shooters who have had to “make do” with military surplus brass for the most part. Lapua says the new brass, both .50 BMG and .221 Fireball, should be in the USA by early April, 2014. Sorry, no pricing info is yet available.
Here is the Lapua Product Announcement for .221 Fireball and .50 BMG Brass:

New 180-Grain and 150-Grain 7mm Scenar-L Bullets
The other big news from Lapua is the release of two new 7mm (.284 caliber) Scenar-L target bullets. Recognizing the popularity of 7mm cartridges among F-Class Open Division shooters, Lapua will offer a high-BC, 180-grain bullet. As part of the “L” series, this new 180-grainer bullet should exhibit extreme consistency in base-to-ogive measurements and bullet weight. We expect this new 180gr projectile to be extremely accurate in the .284 Winchester, .284 Shehane, 7mm WSM, and 7mm RSAUM — popular chamberings for F-Class and long-range benchrest shooters. No BC information has been released yet, but we expect the BC number to be quite high, giving this bullet great wind-bucking capability. In addition to the new 180gr 7mm Scenar-L, Lapua will offer a new 150gr 7mm bullet. This is optimized for medium range competition in Silhouette and Across-the-Course competition. It should offer great accuracy, but with less felt recoil than its 180-grain bigger brother.

|



























 Content of all kinds is going digital, and that includes Reloading manuals. Now Hornady is offering an eBook version of the
Content of all kinds is going digital, and that includes Reloading manuals. Now Hornady is offering an eBook version of the  On his
On his 










