How Bullet Velocity Is Affected by Barrel Twist Rate — Litz Test

Many barrel-makers mark the twist rate and bore dimensions on their barrel blanks.
Does muzzle velocity change with faster or slower barrel twist rates? Absolutely, but much less than you might think. Faster twist rates do slow down bullets somewhat, but the speed loss is NOT that significant. With Bartlein .308 Win barrels of identical length and contour, a 1:12″-twist barrel was only 8 fps faster than a 1:8″-twist barrel. That was the result of testing by Applied Ballistics.
The Applied Ballistics team tested six (6) same-length/same-contour Bartlein barrels to observe how twist rate might affect muzzle velocity. This unique, multi-barrel test is featured in the book Modern Advancements in Long Range Shooting, Vol. 1. That book includes other fascinating field tests, including a comprehensive chronograph comparison.


Barrel Twist Rate vs. Velocity — What Tests Reveal
by Bryan Litz
When considering barrel twist rates, it’s a common belief that faster twist rates will reduce muzzle velocity. The thinking is that the faster twist rate will resist forward motion of the bullet and slow it down. There are anecdotal accounts of this, such as when someone replaces a barrel of one brand/twist with a different brand and twist and observes a different muzzle velocity. But how do you know the twist rate is what affected muzzle velocity and not the barrel finish, or bore/groove dimensions? Did you use the same chronograph to measure velocity from both barrels? Do you really trust your chronograph?
Summary of Test Results
After all the smoke cleared, we found that muzzle velocity correlates to twist rate at the average rate of approximately 1.33 FPS per inch of twist. In other words, your velocity is reduced by about 5 FPS if you go from a 1:12″ twist to a 1:8″ twist. — Bryan Litz
Savage Test Rifle with Six Bartlein Barrels

Most shooters don’t have access to the equipment required to fully explore questions like this. These are exactly the kinds of things we examine in the book Modern Advancements in Long Range Shooting, Vol. 1. In that book, we present experiments conducted in the Applied Ballistics lab. Some of those experiments took on a “Myth Buster” tone as we sought to confirm (or deny) popular pre-conceptions. For example, here’s how we approached the question of barrel twist and muzzle velocity.
Six .308 Win Barrels from Bartlein — All Shot from the Same Rifle
We acquired six (6) barrels from the same manufacturer (Bartlein), all the same length and contour, and all chambered with the same reamer (SAAMI spec .308 Winchester). All these barrels were fitted to the same Savage Precision Target action, and fired from the same stock, and bench set-up. Common ammo was fired from all six barrels having different twist rates and rifling configurations. In this way, we’re truly able to compare what effect the actual twist rate has on muzzle velocity with a reasonable degree of confidence.
Prior to live fire testing, we explored the theoretical basis of the project, doing the physics. In this case, an energy balance is presented which predicts how much velocity you should expect to lose for a bullet that’s got a little more rotational energy from the faster twist. In the case of the .30 caliber 175 grain bullets, the math predicts a loss of 1.25 fps per inch-unit of barrel twist (e.g. a 1:8″ twist is predicted to be 1.25 fps slower than a 1:9″ twist).
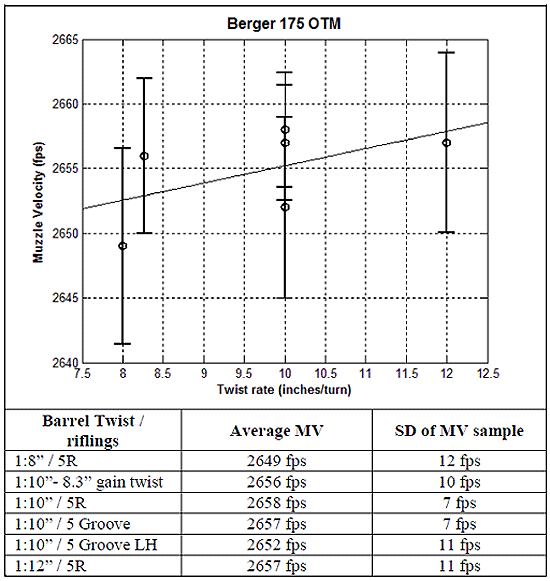
Above, data shows relationship between Twist Rate and Muzzle Velocity (MV) for various barrel twist rates and rifling types. From fast to slow, the three 1:10″ twist barrels are: 5R (canted land), 5 Groove, 5 Groove left-hand twist.
We proceeded with testing all 6 barrels, with twist rates from 1:8″ to 1:12″. After all the smoke cleared, we found that muzzle velocity correlates to twist rate at the average rate of approximately 1.33 fps per inch of twist. In other words, your velocity is reduced by about 5 fps if you go from a 1:12″ twist to a 1:8″ twist. [Editor: That’s an average for all the lengths tested. The actual variance between 1:12″ and 1:8″ here was 8 FPS.] In this case the math prediction was pretty close, and we have to remember that there’s always uncertainty in the live fire results. Uncertainty is always considered in terms of what conclusions the results can actually support with confidence.
 This is just a brief synopsis of a single test case. The coverage of twist rates in Modern Advancements in Long-Range Shooting Vol. 1 is more detailed, with multiple live fire tests. Results are extrapolated for other calibers and bullet weights. Needless to say, the question of “how twist rate affects muzzle velocity” is fully answered.
This is just a brief synopsis of a single test case. The coverage of twist rates in Modern Advancements in Long-Range Shooting Vol. 1 is more detailed, with multiple live fire tests. Results are extrapolated for other calibers and bullet weights. Needless to say, the question of “how twist rate affects muzzle velocity” is fully answered.
Other chapters in the book’s twist rate section include:
· Stability and Drag — Supersonic
· Stability and Drag — Transonic
· Spin Rate Decay
· Effect of Twist rate on Precision
Other sections of the book include: Modern Rifles, Scopes, and Bullets as well as Advancements in Predictive Modeling. This book is sold through the Applied Ballistics online store. Modern Advancements in Long Range Shooting is also available as an eBook in Amazon Kindle format.














 Headspace Gauges
Headspace Gauges




